Responding to Climate Change
Initiatives for the TCFD Recommendations
Formulated in February 2022, the Star Micronics Group’s Sustainability Policy is based on the concept of the Company and employees growing together and contributing to society. In putting into practice this fundamental concept, we recognize the importance of not only the economic, but also the social and environmental aspects of our business activities as we help bring about a sustainable society and enhance corporate value. As a company that operates in countries and regions throughout the world, we also recognize the critical need to address such issues as climate change. In order as a group to meet the expectations and demands of our stakeholders, we have identified and are promoting initiatives to address climate change by reducing CO2 emissions and create environmentally friendly products as material priority issues.
Against this backdrop, the Star Micronics Group expressed its support for the recommendations of the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) in February 2023. With this in mind, we are promoting initiatives to analyze the impact of climate change on our business, together with subsequent risks and opportunities, based on a variety of scenarios. We are then reflecting our findings in business strategies.

Governance
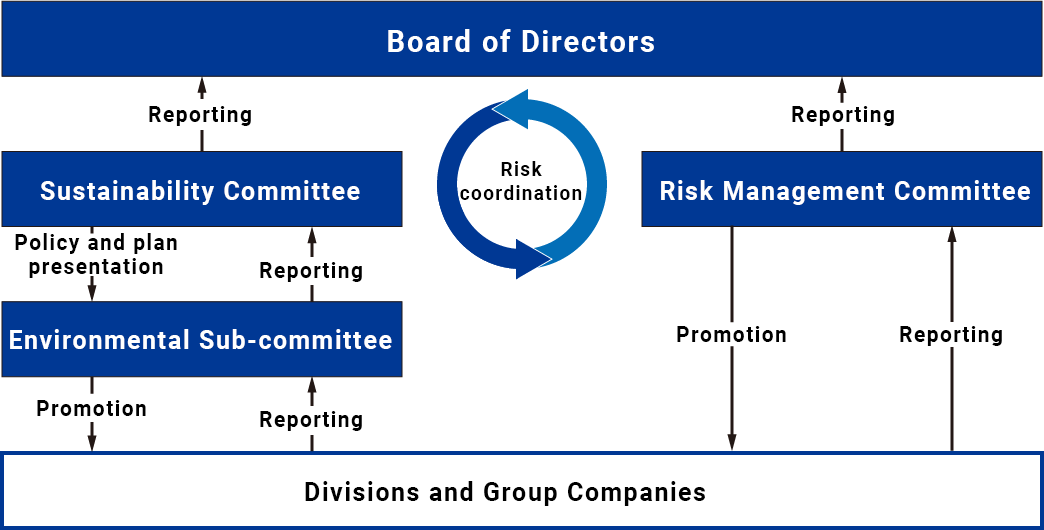
The Group established the Sustainability Committee as a body to make decisions on important matters related to climate change. Chaired by the representative director, President and CEO, and comprised of full-time directors and executive officers, the Committee identifies material sustainability issues, including climate change, sets targets for the resolution of these issues, and promotes Groupwide initiatives. Details of decisions made by the Sustainability Committee as well as counter and related measures are disseminated to each division and Group company through the subordinate Environmental Sub-committee.
The results of activities at each division and Group company are regularly reported to the Sustainability Committee through the Environmental Sub-committee to enhance efficacy and implementation.
As a part of the oversight function, the Sustainability Committee reports regularly to the Board of Directors on the performance and progress of activities.
(Environmental Management Framework)
(Environmental Management Framework Meeting Structure)
| Meeting structure | Main role | Composition | Frequency | 2023 Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Board of Directors |
|
All Board members | In principle monthly | 11 times |
| Sustainability Committee |
|
Chairperson: Representative Director, President and Chief Executive Officer Committee members: Full-time directors and executive officers |
Semi-annually (extraordinary sessions held as required) |
3 times |
| Environmental Sub-committee |
|
Members selected in each division | Semi-annually (extraordinary sessions held as required) |
3 times |
| Risk Management Committee |
|
Chairperson: Representative Director, President and Chief Executive Officer Committee members: Full-time directors and executive officers |
Semi-annually (extraordinary sessions held as required) |
2 times |
Risk Management
Climate change risks are evaluated and managed by the Sustainability Committee. Information is also shared with the Risk Management Committee as necessary.
While climate change risks are identified by the Sustainability Committee, the Environmental Sub-committee evaluates the impact of these risks and considers countermeasures, which are then rolled out to each division and Group company.
The results of the Sustainability Committee’s deliberations are regularly reported to the Board of Directors, which advises and supervises the Sustainability Committee’s efforts.
Strategies
The Star Micronics Group adopts a medium- to long-term approach when conducting scenario analyses to identify climate change risks and opportunities. In this manner, every effort is made to properly reflect the impact of risks and opportunities in strategic plans.
In specific terms, the Group refers to scenarios* published by the International Energy Agency (IEA) and the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) aimed at achieving the objective put forward under the Paris Agreement of holding the average increase in global temperatures to well below 2°C above pre-industrial levels and pursuing efforts to limit the temperature increase to 1.5°C. Accordingly, the Group is conducting two analyses, based on a 1.5°C scenario and a 4°C scenario that assumes greenhouse gas emissions at the current level, to assess the significance of the impact on business activities.
* Main reference scenarios
・1.5℃ scenario: IEA NZE, IPCC 1-1.9
・4℃ scenario : IPCC SSP5-8.5
(Risks and Opportunities Identified)
| Classification | Item | Financial Impact | Countermeasures | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.5 ˚C | 4 ˚C | ||||
| Transition Risk | Introduction of a carbon tax | Surge in commodity prices and an increase in costs fueled by higher direct and indirect expenses owing to the introduction of a carbon tax. | Large | Small |
|
| Tighten GHG emissions regulations | Increase in various costs (including capital expenditures and R&D expenses) in line with efforts to comply with environmental regulations | Large | Small |
|
|
| Change in the energy mix | Increase in energy costs commensurate with a decrease in the share of fossil energy | Medium | Small |
|
|
| Customer reputation | Decrease in sales due to changes in customer needs and product demand as a result of fluctuations in the weather | Medium | Small |
|
|
| Investor reputation | Increase in costs associated with the disclosure of information on efforts to address environmental and other issues | Medium | Small |
|
|
| Physical risks | Increase in average temperatures | Increase in facility management, utility, and other costs associated with rising temperatures | Small | Medium |
|
| Intensification of extreme weather conditions | Decrease in sales and increase in restoration costs due to the shutdown of production plants and supplier damage attributable to floods and torrential rains | Medium | Large |
|
|
| Opportunities | Products and services | Increase in sales owing to the market release of products that comply with regulations and upswing in demand | Large | Small |
|
| Incidence of new component machining needs in line with the shift to EVs; increase in sales on the back of optimal processing machine sales | Large | Small |
|
||
| Resource efficiency | Decrease in manufacturing costs due to switch to energy-saving equipment and improved operating efficiency | Medium | Small |
|
|
| Intensification of extreme weather conditions | Increases in demand for air conditioning equipment as well as orders for machine tools from plants producing related parts resulting in higher sales | Small | Medium |
|
|
| Increase in sales on the back of steps taken to strengthen the service structure and systems and growing reputation among customers for prompt after-sales service | Medium | Large |
|
||
Indicators and Targets
- Indicators
- The Star Micronics Group uses greenhouse gas emissions as an indicator to manage climate-related risks and opportunities.
- Targets
- The Star Micronics Group has set targets for the reduction of scope 1 and 2 GHG emissions of 46% in 2030 compared with 2013 and virtually zero emissions by fiscal 2050. To this end, the Group is promoting reductions in greenhouse gas emissions in a bid to achieve the 1.5°C scenario.
As part of this effort, Star Micronics has been promoting the selection and concentration of its global production base network and is working to improve productivity since 2013. Through these and other means, the Group is endeavoring to reduce GHG emissions.
Looking ahead, plans are in place to renew domestic production bases. The Group is committed to strengthening measures aimed at achieving reduction targets. These efforts include the use of renewable energy while striving to improve production efficiency by introducing energy-saving equipment and promoting DX. - Results
- Results in reducing scope 1 and 2 GHG emissions are presented as follows.
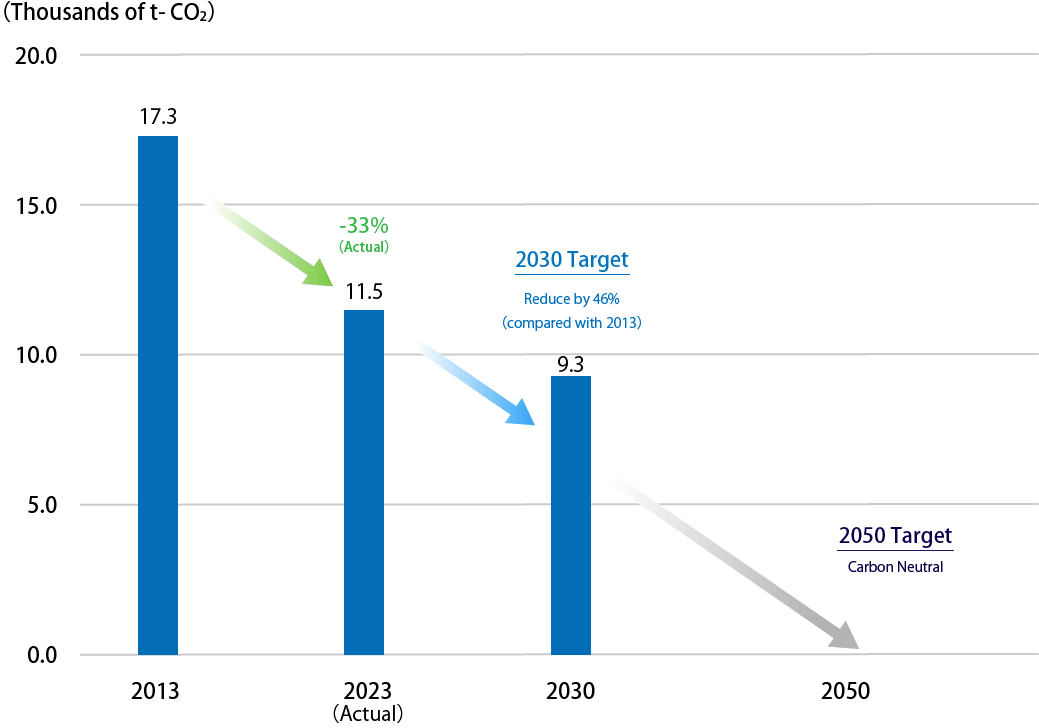
* Scope 1 and 2, including non-consolidated and major consolidated subsidiaries
* Taking into consideration such factors as the review of calculation rules in 2023 and subsequent recalculation, including past performance results, published data has been changed.
Efforts Towards Achieving CO2-Free Operations at Domestic Factories
- Introduction of Renewable Energy
- At our Kikugawa Factory and Star Metal (a subsidiary), which are domestic production bases for our machine tools business, we have switched to CO2-free renewable energy in our efforts to realize a decarbonized society. These two sites account for approximately 70% of the total CO2 emissions of the Star Micronics Group in Japan (2023 actual value), so a significant reduction effect is expected.
- Efforts to Reduce Energy Consumption
- Even after the introduction of CO2-free electricity, we will continue to strive to reduce energy consumption associated with our business activities.
- Environmental Considerations in the Design of Kikugawa South Factory
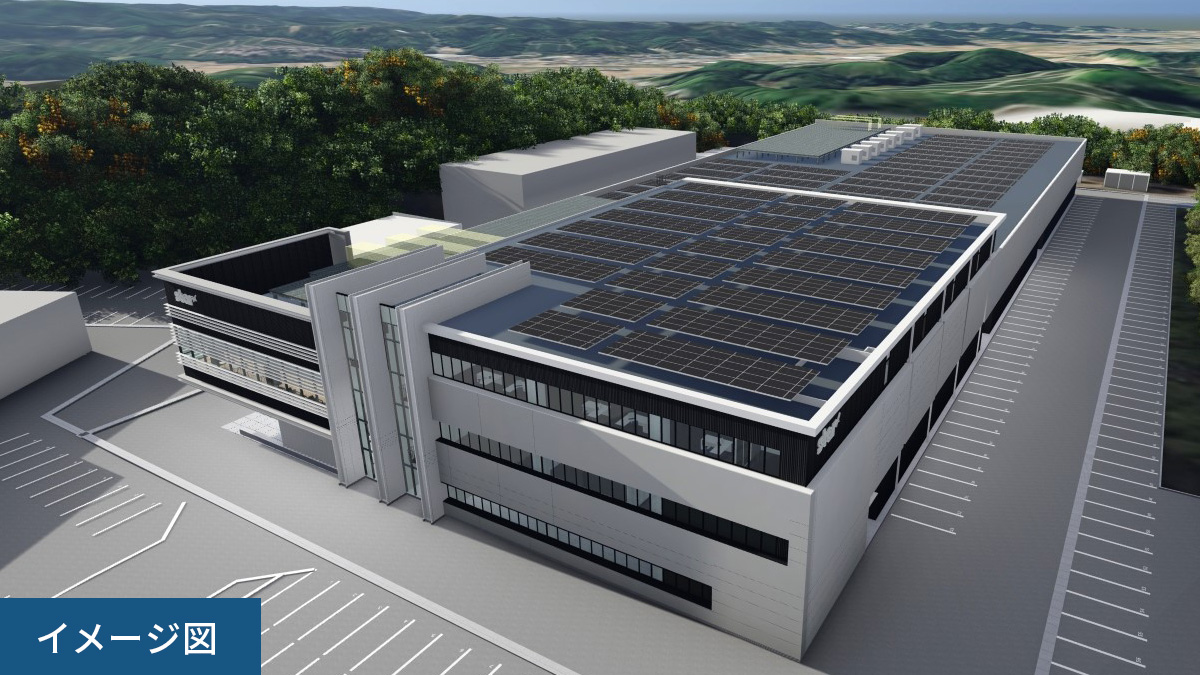
- The Kikugawa South Factory (tentative name), scheduled for completion in November 2025, has obtained both the ZEB*1 certification and the highest S rank under the CASBEE evaluation method*2, which are indicators of energy-saving performance according to the Building-Housing Energy-efficiency Labeling System (BELS).
As a factory designed with environmental consideration, it aims to enhance energy use efficiency by incorporating features such as a high insulation performance exterior envelope (walls, roof, and windows), highly efficient air conditioning equipment, and earth tube facilities*3 that utilize geothermal heat. Additionally, approximately 800kW of solar power generation panels will be installed on the roof. The design and equipment are intended to achieve high levels of energy conservation and energy creation, with the plan to reduce primary energy consumption.
- Efforts Towards Achieving CO2-Free Operations Both Domestically and Internationally
- In addition to promoting CO2-free operations at our domestic factories, we will also aim to achieve CO2-free operations at our overseas factories in the future. We are committed to reducing environmental impact from a global perspective.
*1 The abbreviation for Net Zero Energy Building, the aim is for a building to achieve a zero balance in its annual primary energy consumption, and for its performance to be certified by designated organizations under the BELS certification system, a system for indicating the energy-saving performance of buildings. Standards are set for the amount of energy required by conventional buildings for each building use, buildings being broadly classified into four levels depending on the reduction rate from that standard, with ZEB being the highest rank.
*2 Developed under a Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism and The Institute for Built Environment and Carbon Neutral for SDGs (IBECs) as the Comprehensive Assessment System for Built Environment Efficiency, this system comprehensively evaluates the environmental performance and quality of buildings. Environmental performance efficiency is calculated based on evaluation items that include a building’s environmental quality and performance as well as features designed to reduce its environmental impact. A system by which designated institutions conduct evaluations and certify properties using a five-level ranking, from C the lowest to S the highest.
*3 Equipment that pumps outside air into rooms via pipes buried underground. Underground, the temperature remains stable throughout the year, and the load placed on heating and cooling systems is reduced by bringing the cold air of winter and the hot air of summer closer to the underground temperature as it passes through the ground.

